What is the projected topline number and economic landscape for FY24?
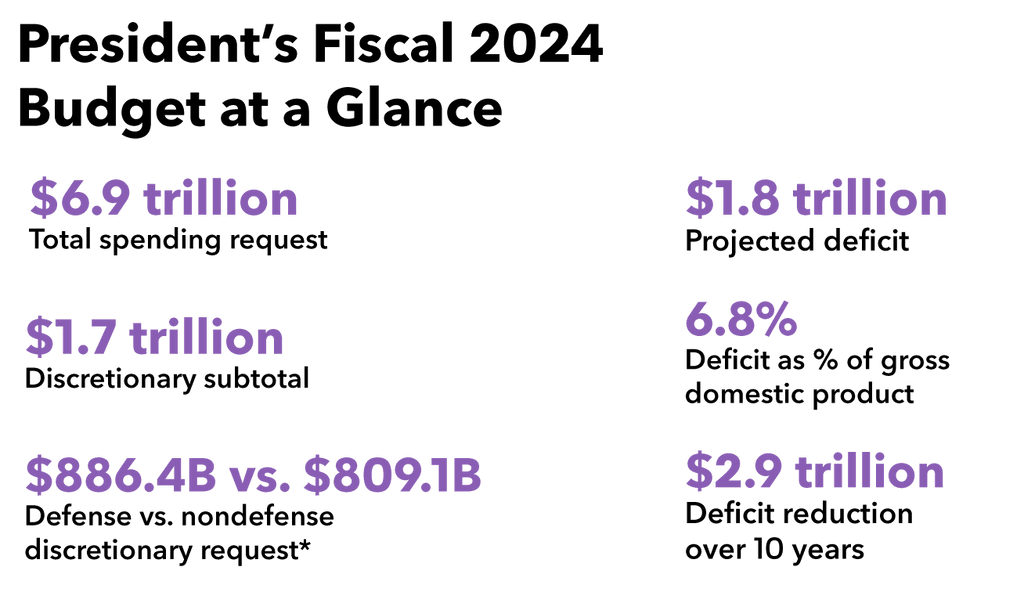
On March 9, 2023, the Biden administration released the proposed federal budget for FY24, which lays out the recommended funding levels for agencies and programs. The proposed FY24 budget is $6.9 trillion, which is a $1.1 trillion increase from FY23’s proposal. GOP officials have criticized the FY24 budget for a high deficit-to-GDP ratio, tax proposals for high-income earners, and monies allocated for mandatory spending. In the coming weeks, Republican lawmakers are projected to write and release their own budget proposal, with expected cuts to federal spending.
Biden’s budget proposal outlines changes in federal spending and taxes that would reduce the deficit by about $3 trillion over a decade. The administration’s request projects that inflation will cool to 4.3% by the end of 2023 and then drop to 2.3% in future years, which is comparable to what economists are forecasting. Also aligned with private estimates, the Biden economic team projects that the U.S. economy will expand .6% in 2023 and 1.5% in 2024.
What are some of the biggest proposed legislative changes to watch in FY24?
A host of tax changes is at the center of the Biden administration’s deficit reduction plan. Some of the biggest changes would apply to investors and high-income taxpayers. Biden’s proposal almost doubles the rate of capital gains tax to 39.6% from 20% for people earning $1 million+ and applies a surcharge for Medicare, which would increase the 3.8% tax enacted under Obamacare to 5% for those earning over $400K. These two proposals taken together would mean that some of the wealthiest taxpayers would pay about a 45% federal rate on their investment income and other earnings.
What are the proposed mandatory funding priorities for FY24?
Under the proposed FY24 budget, mandatory funding priorities include improving health care, education, and childcare. Biden intends to raise Medicare tax rates to 5% for persons making above $400k to extend Medicare’s trust fund solvency by 25 years. To further bring down Medicare spending, he proposes to expand drug pricing changes that were included in the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022. This would include extending the inflation rebates to the commercial market and expanding the number of drugs that will face government negotiations. The Biden administration also hopes to expand access to childcare and universal preschool, in addition to providing free community college and paid family and medical leave.
What are the proposed discretionary funding priorities for FY24?
Defense spending would rise 3.3% and nondefense spending 6.5% in FY24. Within the $886 billion budgeted for defense, the DOD would be the largest recipient of funds; however, monies would also be allocated to other agencies, like the DOE’s nuclear programs. Biden’s FY24 proposes to allocate $1.7 trillion among cabinet-level departments. Education would get a 13.6% increase, HHS would get a 11.4% increase, Treasury would get a 15% increase, the EPA would get a 19.2% increase, and the National Science Foundation would get an 18.6% increase.

[Stay up-to-date on DOD budget priorities and contracting opportunities.]
What are key agencies to watch in FY24?
Defense
The White House proposed $842 billion for defense for FY24, which is a 3.2% increase from last year. Focus would be on deterring China’s influence in the Pacific region, shoring up nuclear defenses, and providing support to Ukraine. If passed, the DOD would receive one of the largest-ever peacetime budgets when adjusted for inflation. The president proposes $37.7 billion for the DOD to maintain the nuclear deterrent triads, including missiles and submarines; $9.1 billion for the Pacific Deterrence Initiative to support allies in the region; and $6 billion to support Ukraine, NATO, and regional partners to counter Russia. In the proposal, there is a suggested 5.2% pay increase for servicemembers and the civilian workforce, in addition to fully funded recommendations from the review of sexual assault in the military.
Health and Human Services
The Biden administration is seeking $144 billion – an 11.5% increase in spending – for the largest nondefense discretionary agency. $22.5 billion would go toward existing early care and education programs, and $13.1 billion is allocated for Head Start, a $1.1 billion increase since last year. The proposed FY24 budget has $7.3 billion for the Office of Refugee Resettlement, plus an emergency contingency fund to give additional resources if there is an unanticipated increase in the number of unaccompanied children and other refugees into the U.S. There would be a 79% increase to the Title X Family Planning program, and $10.5 billion in discretionary funds for public health capacity at CDC and states.
Homeland Security
The proposed budget for Homeland Security is $60.4 billion. In the Trump administration, funds for this department were contended, as there was a fight over funding for the border wall and security. With a GOP majority in the House, this is set to be another contentious area, with major disagreements over how to respond to migrant surges and encounters at the U.S.-Mexico border. This budget calls for about $25 billion for Customs and Border Protection (CBP) and Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), including $535 million for border security technology for ports of entry and funds to hire 350 border patrol agents. There is also $4.7 billion for a new contingency fund to respond to migration surges along the Southwest border. The idea is that Congress would appropriate money incrementally and then CBP and other agencies will be able to draw on those funds to respond to surges as they arise. $865 million would go to U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) to reduce the immigration benefit request backlog and improve processing to advance the administration’s goal of admitting 125,000 refugees.
Treasury
From FY23 to FY24, the Treasury is slated to increase by 15%, with a proposed budget of $16.3 billion. The budget calls for $14.1 billion for the IRS alone, which is a $1.8 billion increase from last year. $642 million would be allocated toward expanding customer service outreach and taxpayer experience, and $290 million would go toward the IRS business systems modernization to accelerate their digital tools. $341 million would be budgeted for the Community Development Financial Institutions (CDFI) fund to provide low-income and underserved communities access to credit, capital, and financial support. $332 million would go to restoring staffing to the core police offices to 2016 levels.
Environment Protection Agency
The EPA has a record-high proposed budget of $12.1 billion, showing a 19.2% increase from last year. Republican officials are already pushing back. The funding would go toward a range of environmental priorities, including $5 billion for greenhouse gas emission reductions and climate resiliency, $4 billion for drinking water infrastructure upgrades, $1.8 billion for environment justice initiatives like Justice40, $356 million for the Superfund program to clean up contaminated lands, $219 million for lead service line replacement, $170 million for PFAS remediation and research, and funds to hire 2,400 employees.
How does the proposed FY24 budget compare to FY 23’s budget?
The proposed FY24 budget is a $1.1 trillion increase from FY23’s budget. The Biden Administration seeks a proposed 7% growth in non-defense discretionary spending in FY24, which would expand such federal programs as child tax credits, tuition reduction, clean energy infrastructure, biomedical and environmental research, and more. From FY23 to FY24, there’s also a proposed 3% increase in defense discretionary spending, with a focus on deterring China’s influence and providing support to Ukraine.
In the FY23 budget, Biden outlined plans to reduce the deficit by nearly $3 trillion over the next decade by increasing taxes for those who make over $400K a year. In light of the ongoing debt ceiling crisis, the President has placed an even more central focus on deficit-reduction goals in his proposed FY24 budget. Under Biden’s FY 24 proposal, Americans earning over $1million+ per year would pay a 39.6% capital gains tax and would see a surcharge for Medicare.
What is included in Biden’s FY23 budget?
On Dec. 23, 2022, the House and Senate passed the $1.7 trillion federal budget for FY23. The FY23 budget includes $772.5 billion for nondefense discretionary programs and $858 billion for defense, with $44.9 billion allocated for Ukraine. After weeks of negotiation between parties, the omnibus aims to advance bipartisan priorities, such as infrastructure, education, nutrition, and affordable housing.
Navigating the federal budget with Bloomberg Government
Bloomberg Government is a comprehensive platform that offers resources on effectively navigating the federal budget. Our news and analysis cover agency funding, historical spending trends, proposed budgets, and appropriations bills, which, together, provide insight into budgetary priorities of various industries. With our legislative tracker, you can stay informed on committee actions and voting decisions that will help you anticipate developments of evolving budgetary landscapes. Request a demo.
